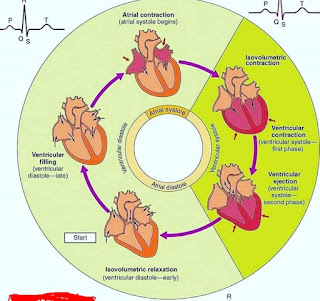
The cardiac cycle refers to the sequence of events that occur and repeat with each heartbeat. It can be divided into two main stages: Systole and diastole, each of which is divided into several small steps When systole and diastole are not specified otherwise refers to ventricular contraction and relaxation Respectively, Reminder Blood flows from low to low pressure Compression increases the pressure in a Chamber, while relaxation reduces the pressure.
When the AVT valves open the anterior pressures are higher than the ventricular pressures and Off when the pressure gradient is reversed.
Similarly, Semiluna valves open when ventricular pressure exceeds submerged /, pulmonary pressure And stop. If the opposite is true, The cycle was started by firing shots at the SA node, which encouraged the atria to lower .
Learn here Atrial Fibrillation Treatment
Learn here Atrial Fibrillation Treatment
It is represented by p-waves in the ECG Shortly after the onset of the P-wave atrial contraction begins and increases the pressure in the area Forcing blood into the ventricles. In the case of atrial contraction, ventricular filling is only for FRACTION. This is because the ventricles are already almost full due to the inactive blood flow down at the moment, Ventricles through open AV valves.
Atrial contraction causes the pressure in the atria to decrease. Reversing the pressure gradient across the AV valves, causing them to close. The termination of the AV valve makes the first sound of the heart S1 And marks the beginning of the systole At the moment.
Ventricular degeneration Halfway through the representation by the QRS complex and the ventricles begin to contract, Creating pressure inside the ventricle for a moment for rapid semilunar, The valves remain closed and the ventricles contract between the closed spaces.
This stage is referred to as isovolumetric contraction. This is because no blood comes out and the ventricular volume remains unchanged. Ventricular ejection begins when the ventricular pressure exceeds the pressure between the joint and the pulmonary. The arteries and pulmonary valves remain open and blood flows out of the ventricles.
This is as fast as the ejection episode, Ventricular repolariization T begins to be reflected by the wave. Ventricular pressure begins to fall and the energy of ejection decreases When ventricular pressure drops below cosmic and pulmonary pressure.
The semilunar valve closes Marks the end of the systole and the beginning of the diastole Semilunar valve closure produces a second heart, sound S2, The first part of diastole again Isovolumetric, because the ventricles relax by closing all the valves.
Ventricular pressure decreases rapidly, but their volume remains unchanged. Meanwhile, the atria are filling with blood, and the pressure of the atria is slowly increasing. Ventricular filling begins when the ventricular pressure drops below the atrial pressure due to the opening of the AV valve
Inactively allows blood to flow from the ventricles, The atria contract and repeat the cycle to end the filling episode.
Hi Admin!
ReplyDeleteThanks for sharing informational blog post. Keep it up. For more information click this hyperlink cardiac cycle